Exploring Portrait Art
 Portrait art captures more than just a face; it immortalizes the essence, emotions, and stories of individuals across time. From the regal depictions of pharaohs in ancient Egypt to the introspective self-portraits of Van Gogh, this art form has evolved, adapting to the cultural, technological, and artistic shifts of each era. It's a window into the soul, offering a glimpse into the sitter's life, the artist's perception, and the period's societal norms.
Portrait art captures more than just a face; it immortalizes the essence, emotions, and stories of individuals across time. From the regal depictions of pharaohs in ancient Egypt to the introspective self-portraits of Van Gogh, this art form has evolved, adapting to the cultural, technological, and artistic shifts of each era. It's a window into the soul, offering a glimpse into the sitter's life, the artist's perception, and the period's societal norms.
Portrait art is not merely about replication but about capturing a moment, an emotion, or a thought, rendered immortally on canvas or through contemporary mediums like giclee prints. These high-quality reproductions allow the beauty and detail of portraits to be accessible in homes, galleries, and collections, preserving the legacy of portrait art for future generations.
Table of Contents
-
Introduction to Portrait Art
- Overview and significance of portrait art
-
The Evolution of Portrait Art
- From Ancient Origins to the Renaissance
- Baroque to Rococo: Dramatic and Whimsical Portraits
- Modern and Contemporary Portraits: Breaking Traditions
-
Famous Examples of Portrait Art
- Frida Kahlo's Self-Portraits
- Rembrandt's "The Night Watch"
- Whistler’s Mother
- Van Gogh's Self-Portraits
-
Techniques and Practical Aspects
- Mastery of Human Anatomy
- The Art of Chiaroscuro
- From Oil Paints to Giclee Prints
-
Practical Tips for Aspiring Portrait Artists
- Starting with a Strong Foundation
- Developing Observational Skills
- Experimenting with Mediums
- Embracing Technology
-
Key Takeaways
- Quick summary of main points
-
Conclusion
- Reflections on the art of portraiture
The Evolution of Portrait Art
 Portrait art has journeyed through the annals of history, mirroring the changing faces of society itself. Initially serving as a means to document and commemorate, it has transformed into a medium for introspection and expression.
Portrait art has journeyed through the annals of history, mirroring the changing faces of society itself. Initially serving as a means to document and commemorate, it has transformed into a medium for introspection and expression.
Ancient Origins to the Renaissance
The transition from rudimentary forms to lifelike depictions marked the Renaissance as a pivotal era in portrait art. Artists began to explore perspective, light, and shadow, crafting images that seemed to breathe life.
Baroque to Rococo: Dramatic and Whimsical Portraits
The Baroque period introduced drama and grandeur, with artists like Caravaggio using chiaroscuro to add depth and emotion. In contrast, the Rococo era, with its light motifs and whimsical themes, offered a playful take on portraiture, reflecting a societal shift towards leisure and frivolity.
 Modern and Contemporary Portraits: Breaking Traditions
Modern and Contemporary Portraits: Breaking Traditions
The advent of photography and later digital techniques, including giclee printing, revolutionized portrait art. Artists were no longer bound to realistic depictions, venturing into abstract and expressive territories to capture the essence of their subjects beyond mere physical resemblance.
Famous Examples of Portrait Art
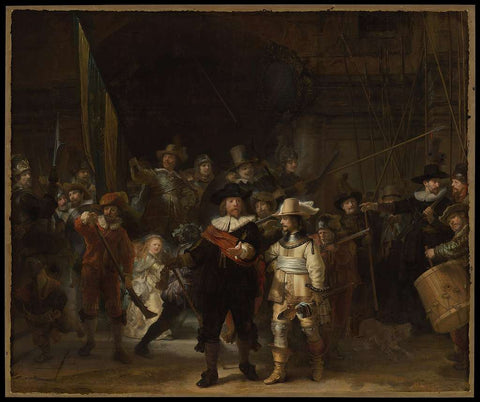 Portraits that have stood the test of time, like Frida Kahlo's "Self-Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird," Rembrandt's "The Night Watch," and Whistler's "Arrangement in Grey and Black No.1," showcase the spectrum of human emotion and the evolution of portrait techniques. These masterpieces highlight the diversity of portrait art, from the deeply personal and symbolic to the grand and communal.
Portraits that have stood the test of time, like Frida Kahlo's "Self-Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird," Rembrandt's "The Night Watch," and Whistler's "Arrangement in Grey and Black No.1," showcase the spectrum of human emotion and the evolution of portrait techniques. These masterpieces highlight the diversity of portrait art, from the deeply personal and symbolic to the grand and communal.
Vincent van Gogh's self-portraits are a profound journey into the psyche of one of art's most complex figures. With over 35 known self-portraits, van Gogh used this medium not out of vanity, but as a means to practice and perfect his art, especially during times when he was financially constrained and lacked models. His self-portraits are not merely representations of his physical appearance but are deeply imbued with his emotional states and artistic explorations.
 One of van Gogh's most iconic self-portraits is the "Self-Portrait with Bandaged Ear," painted in 1889 shortly after the distressing incident where he mutilated his own ear. This work, housed at The Courtauld Gallery in London, is a testament to van Gogh's tumultuous mental state and his unyielding dedication to art. The portrait is characterized by its raw expression of pain and resilience, with van Gogh not shying away from depicting the bandaged ear prominently, a direct nod to his personal turmoil.
One of van Gogh's most iconic self-portraits is the "Self-Portrait with Bandaged Ear," painted in 1889 shortly after the distressing incident where he mutilated his own ear. This work, housed at The Courtauld Gallery in London, is a testament to van Gogh's tumultuous mental state and his unyielding dedication to art. The portrait is characterized by its raw expression of pain and resilience, with van Gogh not shying away from depicting the bandaged ear prominently, a direct nod to his personal turmoil.
Van Gogh's self-portraits from his Paris period (1886–1888) are particularly notable for their exploration of color contrasts and brushwork, marking a significant departure from the dark hues of his Dutch years. These works were instrumental in his development as an artist, showcasing his evolving palette and technique. The "Self-Portrait with Grey Felt Hat" is a vivid example of this period, displaying van Gogh's mastery of color and his unique brushstroke style.
In his self-portraits, van Gogh often depicted himself with an intensity and honesty that is rare in the history of art. His use of color, brushwork, and composition was not just a means of self-representation but also a method of exploring broader artistic concerns. His late works, produced during his time at the asylum in Saint-Rémy, reflect a period of intense self-reflection and experimentation. Despite his declining mental health, these paintings exhibit a remarkable clarity and depth, with van Gogh using his art as a means of coping and understanding his condition.
 Through his self-portraits, Vincent van Gogh offers us a window into his soul, revealing his struggles, his development as an artist, and his enduring quest for understanding and expression. These works stand as a powerful testament to his life and legacy, inviting viewers to look beyond the canvas and connect with the man behind the brushstrokes.
Through his self-portraits, Vincent van Gogh offers us a window into his soul, revealing his struggles, his development as an artist, and his enduring quest for understanding and expression. These works stand as a powerful testament to his life and legacy, inviting viewers to look beyond the canvas and connect with the man behind the brushstrokes.
As we delve deeper into the nuances of portrait painting, from ancient techniques to contemporary innovations like giclee prints, we uncover the timeless allure of capturing the human spirit. Join me as we explore the techniques, challenges, and triumphs of portrait art in the following sections.
Techniques and Practical Aspects of Portrait Art
The creation of portrait art spans centuries, with each era bringing new techniques and insights. Today, artists continue to explore and innovate, blending traditional methods with modern technologies like giclee printing to produce works that resonate across generations.
Mastery of Human Anatomy
Understanding human anatomy is foundational to portrait art. An artist's ability to capture the subtle asymmetry of the human face and the nuances of expression rests on a deep understanding of bone structure, muscle layers, and how light plays across these surfaces. This knowledge allows for the creation of portraits that convey not just the physical likeness but the essence of the subject.
The Art of Chiaroscuro
A technique that has stood the test of time is chiaroscuro, the use of strong contrasts between light and dark to give a sense of volume in modeling three-dimensional objects and figures. This method, perfected during the Renaissance, remains a powerful tool in the portrait artist's repertoire, allowing for the creation of dramatic, lifelike images that seem to leap off the canvas.
From Oil Paints to Giclee Prints
Traditional portrait painting often involves oils, known for their richness and depth of color. Artists layer these paints to create textures and hues that mimic the subtleties of human skin and clothing. In contrast, watercolor offers a lighter, more ethereal quality, often used to capture the spontaneity of a subject's character.
The modern era has introduced digital technologies into the art of portraiture, notably giclee printing. This high-resolution inkjet printing technique allows for the reproduction of artworks with incredible fidelity to the original's color and detail. Giclee prints have democratized art, making high-quality reproductions accessible to a broader audience and offering artists a new medium through which to share their work.
Practical Tips for Aspiring Portrait Artists
-
Start with a Strong Foundation: Begin by sketching the basic shape of the head and shoulders, paying close attention to proportions.
-
Develop Your Observational Skills: Practice capturing expressions and moods by studying subjects in various settings and lights.
-
Experiment with Mediums: Whether it’s traditional oil and watercolor or modern digital painting and giclee prints, exploring different mediums can help you find your unique voice as a portrait artist.
-
Embrace Technology: Use digital tools and techniques to enhance your art. Giclee printing, for instance, can be a great way to reproduce and share your portraits with a wider audience.
Key Takeaways
- Mastery of human anatomy is crucial for realistic portrayals in portrait art.
- Historical and cultural contexts deeply influence the styles and themes of portrait art.
- Techniques have evolved, from oil painting to giclee prints, broadening access to portrait art.
Conclusion
Portrait art is a dynamic and evolving form, reflecting the complexity of human emotion and the depth of individual experience. From the detailed study of anatomy to the mastery of light and shadow, and the embrace of modern printing techniques, the journey of a portrait artist is one of perpetual learning and discovery.
As we continue to explore and appreciate the art of portraiture, let us remember the power of a portrait to capture more than a likeness—to tell a story, evoke an emotion, and celebrate the human spirit.
Would you like more detailed guidance on specific portrait painting techniques or further exploration into modern adaptations such as giclee prints?
References
Images: https://picryl.com/
Art Education: https://theartofeducation.edu/
Art Therapy Science: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9472646/

 Portrait art captures more than just a face; it immortalizes the essence, emotions, and stories of individuals across time. From the regal depictions of pharaohs in ancient Egypt to the introspective self-portraits of Van Gogh, this art form has evolved, adapting to the cultural, technological, and artistic shifts of each era. It's a window into the soul, offering a glimpse into the sitter's life, the artist's perception, and the period's societal norms.
Portrait art captures more than just a face; it immortalizes the essence, emotions, and stories of individuals across time. From the regal depictions of pharaohs in ancient Egypt to the introspective self-portraits of Van Gogh, this art form has evolved, adapting to the cultural, technological, and artistic shifts of each era. It's a window into the soul, offering a glimpse into the sitter's life, the artist's perception, and the period's societal norms. Portrait art has journeyed through the annals of history, mirroring the changing faces of society itself. Initially serving as a means to document and commemorate, it has transformed into a medium for introspection and expression.
Portrait art has journeyed through the annals of history, mirroring the changing faces of society itself. Initially serving as a means to document and commemorate, it has transformed into a medium for introspection and expression. Modern and Contemporary Portraits: Breaking Traditions
Modern and Contemporary Portraits: Breaking Traditions Portraits that have stood the test of time, like Frida Kahlo's "Self-Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird," Rembrandt's "The Night Watch," and Whistler's "Arrangement in Grey and Black No.1," showcase the spectrum of human emotion and the evolution of portrait techniques. These masterpieces highlight the diversity of portrait art, from the deeply personal and symbolic to the grand and communal.
Portraits that have stood the test of time, like Frida Kahlo's "Self-Portrait with Thorn Necklace and Hummingbird," Rembrandt's "The Night Watch," and Whistler's "Arrangement in Grey and Black No.1," showcase the spectrum of human emotion and the evolution of portrait techniques. These masterpieces highlight the diversity of portrait art, from the deeply personal and symbolic to the grand and communal. One of van Gogh's most iconic self-portraits is the "Self-Portrait with Bandaged Ear," painted in 1889 shortly after the distressing incident where he mutilated his own ear. This work, housed at The Courtauld Gallery in London, is a testament to van Gogh's tumultuous mental state and his unyielding dedication to art. The portrait is characterized by its raw expression of pain and resilience, with van Gogh not shying away from depicting the bandaged ear prominently, a direct nod to his personal turmoil.
One of van Gogh's most iconic self-portraits is the "Self-Portrait with Bandaged Ear," painted in 1889 shortly after the distressing incident where he mutilated his own ear. This work, housed at The Courtauld Gallery in London, is a testament to van Gogh's tumultuous mental state and his unyielding dedication to art. The portrait is characterized by its raw expression of pain and resilience, with van Gogh not shying away from depicting the bandaged ear prominently, a direct nod to his personal turmoil. Through his self-portraits, Vincent van Gogh offers us a window into his soul, revealing his struggles, his development as an artist, and his enduring quest for understanding and expression. These works stand as a powerful testament to his life and legacy, inviting viewers to look beyond the canvas and connect with the man behind the brushstrokes.
Through his self-portraits, Vincent van Gogh offers us a window into his soul, revealing his struggles, his development as an artist, and his enduring quest for understanding and expression. These works stand as a powerful testament to his life and legacy, inviting viewers to look beyond the canvas and connect with the man behind the brushstrokes.






